The Essential Guide to the LMS Administrator Role and Responsibilities

In today’s fast-paced corporate landscape, an efficient learning management system is one of the indispensable tools fostering employee growth, meeting compliance requirements, and achieving organizational goals. At the heart of any successful LMS is the LMS administrator—a role that ensures smooth management and optimization of the learning environment. Much like the conductor of an orchestra, the LMS admin harmonizes various elements of the learning ecosystem to deliver a seamless learning experience. If you’re wondering what an LMS administrator does, this guide will provide insights into the role, skills, challenges, and certifications associated with LMS administration in 2025.
LMS Administrator Role
An LMS administrator’s roles and responsibilities combine the functions of an IT systems administrator and a learning manager. Such specialists manage learning technology in an organization, which is sometimes not limited to learning management systems but also includes learning experience platforms. Their responsibilities fall into several categories, which we will review in detail below.
System configuration and management
These functions include setting up, customizing, and maintaining the learning management system to align with the organization’s learning objectives. For instance, an LMS system administrator at a global enterprise ensures that the LMS supports multilingual corporate training programs by setting up language-specific user interfaces, selecting time zones, and managing certificate templates in different languages.
Content management
This group of responsibilities includes uploading, organizing, and updating training materials, courses, and assessments. For example, in a healthcare organization, the LMS administrator uploads mandatory compliance training modules, such as HIPAA or OSHA, and ensures that they are updated annually to reflect changes in regulations. They can also build learning paths for students and manage the general course knowledge base.
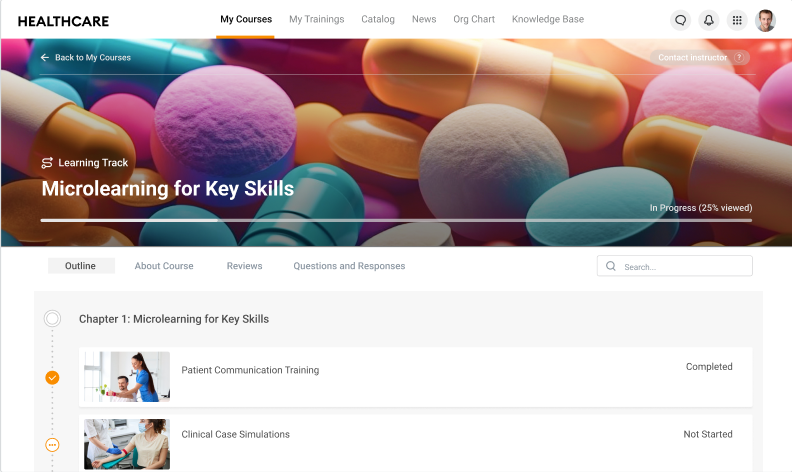
User management
User management includes adding new users and managing user accounts, assigning roles, and ensuring a smooth onboarding process for learners. For example, retail chains with seasonal hires rely on LMS administrators to quickly onboard temporary workers, assigning them relevant training courses based on their roles to ensure they’re ready for peak sales periods.
Data analysis and reporting
Data analysis in a learning management system involves tracking user progress, generating compliance reports, and analyzing training effectiveness, including qualitative elements based on the chosen learning model. For example, at a tech company, the LMS administrator tracks employee completion rates for cybersecurity training and generates detailed compliance reports for auditing purposes.
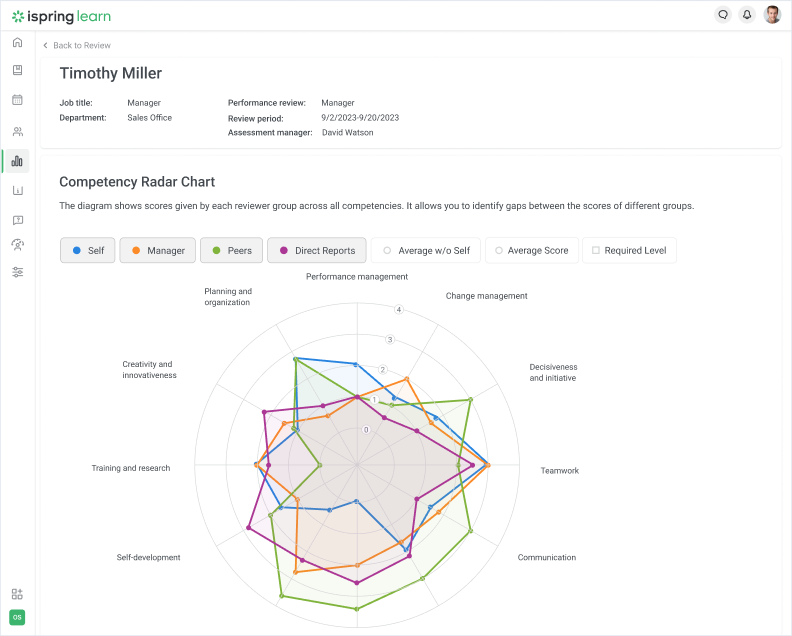
Modern learning management systems offer advanced reporting functions, such as 360-degree feedback, allowing the assessment of an employee’s professional skills by everyone they work with, from subordinates to managers.
Technical support
Technical support includes troubleshooting technical issues, liaising with learning management system vendors, and providing assistance to end-users. For instance, in educational institutions, the LMS administrator resolves login issues for new students and coordinates with the LMS software vendor to address system glitches before the semester begins.
Policy compliance
These duties include ensuring that the learning management system adheres to industry regulations, including data security and accessibility standards. For a financial firm, the LMS administrator configures the platform to ensure GDPR compliance, as by anonymizing user data after a set retention period.
LMS Administration Skills and Qualifications
An LMS administrator must possess a mix of technical expertise, organizational skills, and interpersonal abilities. Here are the key skills and qualifications:
Technical proficiency
A successful LMS administrator should be familiar with LMS platforms, APIs, and integrations. They must understand the technical aspects of LMS implementation, including configuration, integrations, and software updates, to ensure optimal system performance and compatibility with organizational tools.
Data analytics
The ability to interpret learning metrics and generate actionable insights is another aspect of the LMS administrator’s job. By analyzing learner progress and course completion rates, LMS admins identify trends, gaps, and opportunities to enhance training programs and improve overall learning outcomes.
Project management
LMS administrators should be skilled in managing timelines, coordinating stakeholders, and ensuring the successful delivery of learning initiatives. Strong project management skills enable them to align learning projects with organizational goals and deliver solutions by deadlines.
Communication skills
One of the most important requirements for a learning management system administrator is strong written and verbal communication for collaborating with teams and addressing learner queries for user support. Administrators serve as the point of contact for learners, vendors, and leadership, requiring clear communication to resolve issues and gather feedback effectively.
Educational background
An LMS admin would typically have a bachelor’s degree in HR, instructional design, IT, or a related field. A certification in learning management platforms would be a plus. A relevant degree combined with certifications equips these administrators with both theoretical knowledge and hands-on expertise in LMS management.
Challenges in LMS Administration
LMS administrators often face the following challenges:
User engagement
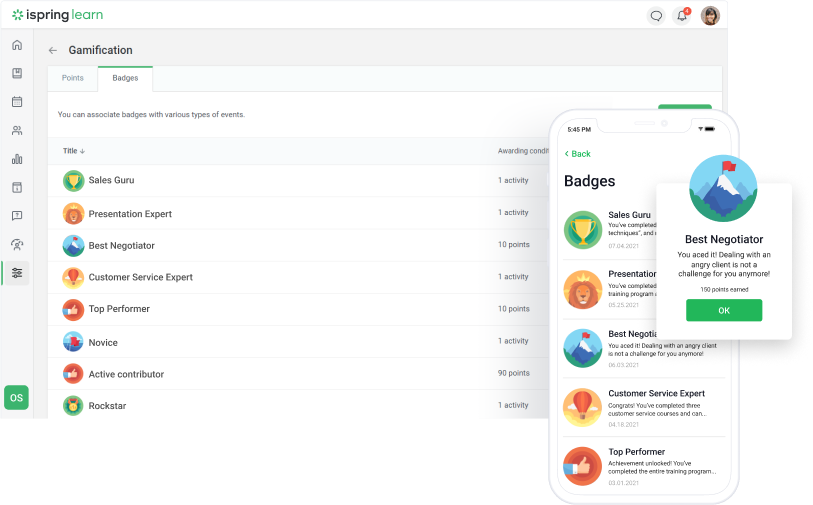
Encouraging employees to participate in training programs can be difficult, especially when learners perceive courses as irrelevant or time-consuming. An LMS administrator must create engaging content, utilize gamification techniques, and ensure that training aligns with employees’ career goals.
System integration
Another challenge is integration between the LMS and other organizational systems, such as HR software or analytics tools. LMS administrators oversee compatibility issues and must work with IT teams to streamline workflows and reduce data silos.
Compliance management
Keeping up with evolving industry regulations and ensuring the LMS meets them requires constant vigilance. LMS admins must monitor changes in compliance standards, update training content, and ensure accurate reporting to avoid legal or financial penalties.
Best Practices in LMS Administration
To address these challenges, LMS administrators can adopt the following best practices:
Continuous learning. Stay updated with the latest LMS functions and trends by participating in training, webinars, and industry events. Keeping up with emerging technologies ensures that an LMS administrator can implement innovations to improve user experience and platform efficiency.
Regular audits. Periodically review and update courses, user data, and system settings to maintain platform relevance. Audits help an LMS administrator identify outdated content, inactive users, and configuration issues that may impact the LMS’s performance.
User feedback. Actively seek feedback from learners and use it to enhance the platform by addressing their concerns and improving usability. Regular surveys, focus groups, and user interviews provide insights into individual learner needs and desirable platform improvements.
LMS Administrator Certifications
LMS administrator training and certifications can enhance their expertise significantly. Popular options include:
- Certified administrator programs: Offered by leading LMS providers like SAP Litmos, Moodle, and Blackboard.
- CompTIA certifications: For technical proficiency in systems management.
- Project Management Professional (PMP): To improve project coordination skills.
- Specialized LMS certifications: Focused training on specific platforms or functionalities.
How to Become an LMS Administrator
Becoming an LMS administrator requires a combination of education, experience, and continuous learning. Here are the steps to take:
- Earn a relevant degree. Earn a bachelor’s degree in fields like education, information technology, human resources, or a related discipline. This provides foundational knowledge in learning systems and organizational processes.
- Gain technical skills. Familiarize yourself with LMS platforms through hands-on experience or self-paced learning. Understanding LMS integrations, APIs, and data reporting tools is a plus.
- Build experience. Start with roles like instructional designer, eLearning coordinator, or IT support to gain experience in learning systems and corporate training environments.
- Pursue certifications. Obtain certifications from leading LMS providers or project management organizations to validate your skills and enhance your expertise.
- Develop soft skills. Strengthen your project management, communication, and analytical skills to better manage stakeholders and improve learner engagement.
- Stay updated: Engage in continuous learning by attending webinars, workshops, and networking events to keep informed about the latest trends in LMS technology and corporate learning.
- Apply for roles. Once equipped with the necessary skills and experience, seek LMS administrator roles in organizations that align with your career goals.
Why is the LMS Administrator Role Important?
LMS administrators ensure that the organization’s learning environment functions well, which directly impacts employee performance, compliance adherence, and overall business outcomes. By optimizing learning management systems and providing technical support, they help reduce training costs, improve learner satisfaction, and drive measurable results. Their role is especially critical in monitoring system performance and ensuring the adaptability of corporate learning programs as business needs evolve.
Conclusion
With modern technological advancements, an LMS administrator becomes an indispensable asset, especially in larger organizations. Their expertise bridges the gap between technology and learning, enabling businesses to develop a culture of continuous improvement. As corporate learning becomes increasingly dependent on data-driven decisions, investing in a skilled LMS administrator is essential for success. Whether you’re implementing an LMS for the first time or enhancing an existing system, recognizing the value of this role will ensure your learning initiatives achieve their full potential.







