9 Essential Topics for Effective Manufacturing Safety Training

Safety training is essential in the manufacturing industry. According to data from the International Labour Organization, manufacturing is among the four most hazardous sectors, which account for 63% of all fatal injuries at work. One of the measures manufacturing businesses can take to improve this sad statistic is upgrading their safety training programs. Of course, creating and launching an effective training program or course is no easy feat — but we’ve got you covered.
In this article, we’ll provide an overview of key manufacturing safety topics, explain how to optimize safety and health training at scale, and answer some frequently asked questions on workplace safety in manufacturing. Plus, we’ll share a list of manufacturing safety training resources that you might find handy. Let’s dive in.
Key Safety Topics for Manufacturing Companies
Workplace safety is an important topic regardless of the industry in which a business operates. Even in an average office, accidents like slips, trips, falls, illnesses, and more, can happen and result in prolonged productivity losses. But in manufacturing, where failing to adhere to safety standards and requirements at the workplace often causes serious injuries or even death, teaching employees how to stay safe while doing their jobs is vital.
According to data collected by OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration), the overall number of severe on-the-job injuries reported from 2015 to 2024 amounted to 91,140 cases. To prevent more tragic occurrences like these, employers must, first and foremost, commit to enforcing safety protocols and providing proper safety training to their staff. This training will help employees increase emergency preparedness and gain the necessary knowledge and skills to do their job safely, as well as to react to potential emergencies quickly and adequately, thus reducing the injury and death toll on the job.
The topics to cover during this training will clearly depend on the processes at the specific manufacturing facility and on the equipment used. For example, car manufacturing plant workers will need more focus on the proper use of mechanical and electrical equipment, while for chemical factory employees, handling hazardous materials will generally be a more relevant topic.
Still, there are some universal manufacturing safety topics that need to be covered to provide comprehensive safety training regardless of the type of manufacturing. Let’s take a closer look at the list below.
1. Equipment usage and maintenance
Incidents involving machinery are one of the major causes of serious injuries in manufacturing. To prevent accidents that can lead to disability or even death, it is crucial to instruct workers on the proper use and maintenance of every piece of equipment they come into contact with at your facility upon hiring.
To keep employees safe, evaluate hazards, explain the potential harm machines can cause, and include comprehensive information on essential safety topics, such as control of hazardous energy (lockout/tagout) and conveyor safety, in your training program.
2. PPE (Personal Protective Equipment)
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is one of the critical safety topics you should never skip to ensure proper training. Make sure every worker is provided with necessary items, such as gloves, goggles, helmets, ear protection gear, etc.; understands how to use them for their intended purpose; and knows when they should wear personal protective equipment at work.
Some essential PPE safety training topics to cover in training courses include storage and maintenance rules, determining the right types of safety gear for each given task, identifying and resolving issues, and the proper use of safety equipment. Assessing PPE usage skills during safety meetings is also a must.
3. Preventing and handling fire hazards
Fire hazards are present in every workplace. At manufacturing facilities, the primary sources of potential hazards include electrical equipment, flammable materials, combustible chemicals, and malfunctioning equipment.
To lower the risks, make sure to take preventive measures: equip your facility with a reliable fire protection system and fire safety gear, implement fire safety protocols, and instruct all workers on adequate fire risk assessment and emergency procedures. Conducting regular fire drills is also essential to protect employees at work.
4. Slips, trips, and falls
Slips, trips, and falls are extremely common in all workplace settings, including manufacturing facilities. Unfortunately, neglecting general requirements for fall protection tops the list of the most commonly violated safety standards.

Specialized equipment, such as harnesses and lifelines, can help reduce the risks, so it’s crucial to make sure that workers have this gear and know how to use it properly. Proper instruction on operating at great heights, ladder safety, and workplace maintenance is also critical to keep employees safe and ensure their well-being.
5. Incident reporting
Sometimes, incidents happen despite all the training and preventive measures taken, especially in the manufacturing industry. In such cases, reporting becomes a critical step to avoid further issues and keep the workplace safe. Thus, incident reporting is one of the key safety topics to cover during training.
Make sure your employees get clear instructions on how to communicate information about accidents, potential hazards, neglect of safety guidelines, safety protocol breaches, etc. Including detailed guidelines on reporting procedures will ensure everyone knows what to do when incidents occur and minimize negative consequences.
6. Hazard communication
The manufacturing industry often uses hazardous chemicals that may cause damage if not handled correctly. According to the Hazard Communication Standard implemented by OSHA, workers must be informed about potential risks through hazard communication, which involves the proper labeling of hazardous materials, and providing reference sheets. Staying compliant with the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals is also required.
As employees are concerned, the core safety topics to focus on in this regard include understanding the labeling of hazardous materials, as well as properly storing and handling them.
7. Hazardous waste management
Hazardous waste is waste that has properties that make it potentially dangerous for humans or the environment. Handling it properly is crucial for maintaining not only your workers’ health and well-being but also for protecting the environment. That’s why storing and utilizing such waste requires thorough adherence to official safety guidelines and regulations.
In the US, hazardous waste management is regulated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). To ensure correct handling of such waste, make sure employees are familiar with the agency’s requirements, understand which materials must be classified as hazardous waste, and know how to stay compliant with all other applicable rules and regulations.
8. Hand safety
Employees at manufacturing facilities use their hands for virtually any task, from gripping tools to pressing machine control buttons. That’s why hand protection is one of the core manufacturing safety topics to cover during training.
To be effective, the course should include information on the most common hand hazards, such as potentially dangerous equipment and substances. You should also make sure employees are aware of safe practices to protect their hands and know how to use personal safety equipment. This will help avoid common hand injuries such as cuts, burns, and bruises, as well as more serious damage, like crushes and amputations.
9. Electrical safety
Electrical safety plays a key role in preventing accidents, especially at facilities with a lot of machinery that relies on electrical systems to function. Neglecting electrical hazards can lead to critical damage to both your employees’ health and the facility’s infrastructure. Moreover, failing to address electrical risks, as well as other safety risks, can result in massive fines from regulatory organizations.
Some of the common safety topics regarding electrical safety include basic electrical safety, proper wiring and grounding, understanding lockout/tagout procedures, recognizing faulty equipment, and reporting it.
How to Launch a Manufacturing Safety Training Program
Ready to deploy a training program to ensure workplace safety at your company? Here are the essential steps to launch an effective manufacturing safety program at any organization.
- Identify training needs and research the relevant topics. Conducting a needs analysis will help you understand the areas to focus on and pick the most relevant safety training topics for manufacturing facilities.
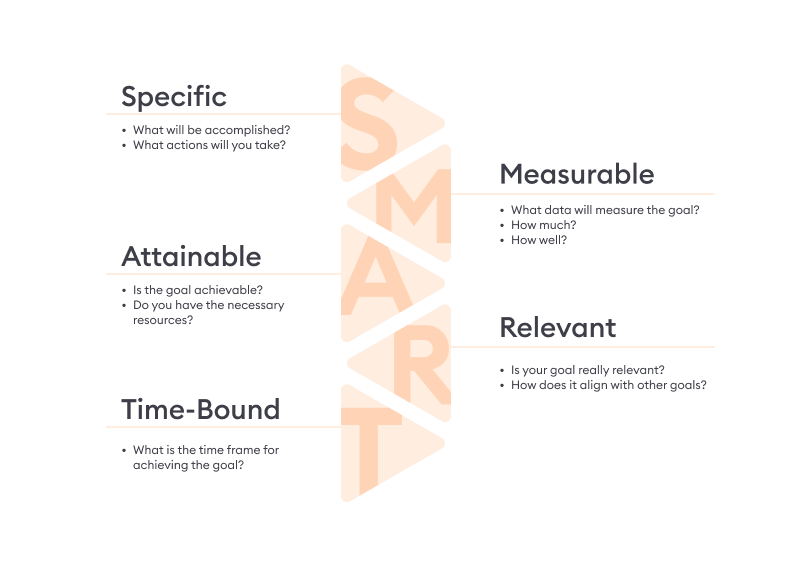
- Define training goals and objectives. What results do you want to achieve with your training programs, and how soon? Use the SMART formula to make sure your goals are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. An example of such a goal would be “Ensure that all factory staff know how to use PPE properly by the end of the quarter.”
- Choose the delivery method. There are several ways to deliver training courses to employees effectively. Depending on your resources, you can choose between instructor-led training, eLearning, or blended learning. Generally, eLearning is the most cost-effective and convenient option, plus online courses are easier to scale. With a software platform, you can easily assign courses, personalize and edit learning content, track progress, and more.
- Outline a training program plan. Now that you’ve defined the destination, create a roadmap. Consider methods of delivery, learning content types, and the evaluation methods you’ll use to make your training successful.
- Select a course creation tool. If you’ve decided on training your employees entirely or partially online, you’ll also need to create digital materials and assemble them into a training program or course. To optimize the process and achieve the best possible result, you’ll need an effective authoring tool that will allow you to include all the necessary materials and piece them together quickly and easily.
iSpring Suite is a great example of such a tool. Just pick a topic and put together a course as you would a puzzle, using texts, images, videos, and interactive quizzes without spending hours and days mastering the tool. No special skills are required: knowing how to work in MS PowerPoint is sufficient. Plus, there’s also a powerful built-in AI feature to supercharge course creation and a cloud-based version for more flexibility. Moreover, iSpring Suite is available bundled with iSpring Learn — a powerful eLearning platform with a user-friendly interface and robust functionality.
Take a look at a 20-minute demo course on fire safety and prevention created with iSpring Suite:
- Create engaging training materials. In the end, your training is only as good as your training materials, so spare no time to create quality content using the authoring tool of your choice. Remember to use a variety of content types and include different training activities to keep learners engaged throughout the course.
Adding a variety of interactive activities to your course helps keep learners engaged and improves learning outcomes.

Also remember that, regardless of the delivery method, your training content should be comprehensive, aligned with your training goals, and in compliance with relevant rules and regulations.
- Collect feedback and improve your materials if necessary. Before you deploy your training full-scale, gather a focus group to try it out and share feedback. Use their comments to identify weak spots and improve your course or program. It’s also worthwhile to include a feedback section in an online course to streamline feedback collection after you make the training program available to all employees.
- Launch your program. Now you’re ready to roll out your safety and health training program. If you opt for an eLearning solution, begin by uploading your training content into an LMS. There, you can create standalone courses or arrange them in learning paths, schedule live safety meetings, and more. Communicate deadlines clearly and highlight mandatory courses for best results.
- Test and evaluate. Finally, remember that assessing results is an essential part of every training program. Add an interactive quiz at the end of each module and wrap up the course with a final test. Analyze the results and make improvements to the program if necessary.alt=An interactive quiz example from a demo course by iSpring

For more comprehensive information, read our article on how to build a manufacturing training program.
4 Ways to Make Your Manufacturing Safety Training More Effective
Here are some best practices you can use to optimize your manufacturing safety training courses.
Use videos
Gone are the days when multi-page instruction manuals were the only resources available. Although reading manuals is still important, the overwhelming majority favor videos for training.
According to research by TechSmith, 83% of people prefer to get instructions or information through videos. Moreover, people enjoy watching videos: only 16% admitted to watching them because they had to. So, if you want to engage employees and make your training effective, use the video format.
Make it bite-size
Bite-size learning, aka microlearning, is a concept based on the idea that information is processed and retained better when it is presented in small, easily digestible “bites.”
Getting information from short tutorials or posts on social media are some illustrative examples. Today, the concept has even been adopted by academic institutions, and it fits corporate training ideally too. Keeping your courses no more than 20 minutes long will ensure that employees don’t lose focus and will improve learning retention.
Leverage mobile learning
Mobile learning has long been on the rise, and it’s still growing. According to a report by GMI, the mobile learning market was estimated to reach a CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) of over 16% in 2024-2032.
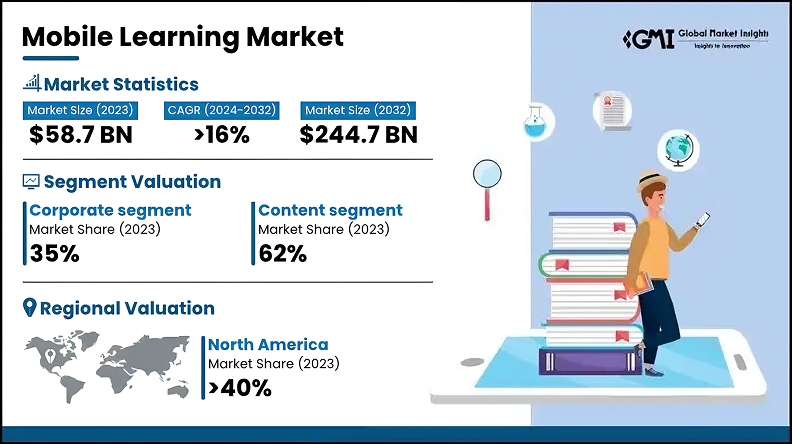
This comes as no surprise, since mobile learning provides accessibility and flexibility that is in high demand in today’s fast-paced world. By making your safety courses mobile-friendly, you can provide more personalized learning experiences, increase learner engagement, and ensure higher course completion rates.
Make it seamless
While mobile learning is a powerful way to provide an enhanced learning experience, don’t forget about other platforms. Making training materials available on any device and accessible from anywhere is the best way to ensure that trainees will use all available opportunities to complete your courses or programs.
But it is also crucial to make the training process as seamless as possible. To achieve this, make sure progress is saved even offline and updated automatically on any device, enabling learners to switch between devices without any inconvenience.
Manufacturing Safety Training Resources
To keep manufacturing safety training at your company relevant and compliant with current standards and requirements, make sure you only use reliable sources when creating training materials. Here is a list of some essential resources you’ll need to consult if your business operates in the US.
- OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration, part of the United States Department of Labor). This is a go-to place for official information on government standards such as laws and regulations, training requirements by standard, etc.
The website also covers some essential safety topics, such as fall protection, personal protective equipment, hazard communication, etc. Plus, you can find information and the key official safety guidelines sorted by industry sector.
- NASP (National Association of Safety Professionals). This US-based organization offers a wide array of courses and accredited certification programs in workplace and environmental safety. Initially provided solely as in-house training, these courses and programs can now be taken online.
The NASP also offers consultative services to safety professionals, plus the website features useful information that will come in handy for course creation on safety training topics.
- NSC (National Safety Council). The NSC is a prominent US-based non-profit dedicated to promoting public health and safety. The organization offers various safety training and certificate programs, such as the NSC Advanced Safety Certificate program, driver training, workplace safety training, first aid training, and more.
The organization is trustworthy and reliable since it has long worked in close collaboration with OSHA.
Important: if your company operates outside of the US, you’ll need to adhere to the safety requirements in the country where your manufacturing facility is located.
For example, in the EU, these are EU-OSHA (The European Agency for Safety and Health at Work, the European analog of OSHA) and ENSHPO (The European Network of Safety & Health Professional Organizations); in the UK, there is HSE (The Health & Safety Executive) and other organizations.
Be sure to consult region-specific resources when preparing your courses and other training materials.
FAQs
What are the 10 safety rules in the manufacturing industry?
While there is no universal fixed list of safety rules for the manufacturing industry, there are some core guidelines you can use to provide a safe workplace to your employees and avoid accidents. We suggest that you be guided by the following:
- Prioritize regular safety training. Make sure your courses and training programs cover all the essential topics relevant to your organization.
- Only use reliable official resources such as OSHA, NASP, and NSC when creating safety training materials.
- Make safety training programs flexible and accessible.
- Hold an in-person or an online safety meeting for your employees every once in a while.
- Regularly test and assess your employees’ knowledge of all relevant safety topics.
- Teach your employees proper risk assessment.
- Pay special attention to hazard communication and incident reporting.
- Create a safe work environment: keep emergency exits clear and doors unblocked, make sure the space is clean and uncluttered, that floors are dry and clean, etc.
- Enforce proper usage of personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Do not allow employees to work until they complete a safety program or course.
This is a sample list that features general recommendations. You can adapt it according to the specifics of your manufacturing facility.
What are the 5 key topics of OSHA?
OSHA provides a list of crucial topics related to safety at work on its official website. The 5 key topics of this list are:
- Fall prevention
- Hazard communication
- Personal protective equipment
- Heat illness prevention
- Trenching and excavation
Additionally, there is a section on the menu that is straightforwardly called “Key topics.” This list contains the following 4 items:
- Recordkeeping requirements and forms
- Safety and health programs
- Support after a loss
- Whistleblower protections
What are the 5 types of safety?
We can define several types of safety that are relevant in any industry, including manufacturing. These are:
- Environmental safety
- Physical safety
- Psychological safety
- Cyber safety
- Health and biological safety
To fully ensure workplace safety at your facility, make sure your training is comprehensive and covers all of the above areas.








