15 Types of Training Programs

After completing your training needs analysis, you’ll need to decide what types of training programs you will develop, from basic orientation training to advanced skill development.
But here’s a concerning trend: only 23% of learners and 22% of leaders say workplace training at their organization is effective.
This article will help you navigate established and emerging types of training to avoid this misalignment. You’ll learn how to make your training more effective by choosing methods that match both your business goals and employee preferences.
For each training type, we share real-world applications, implementation tips, and typical per-learner budget ranges that companies adopt.
What Are the Various Types of Effective Employee Training Programs?
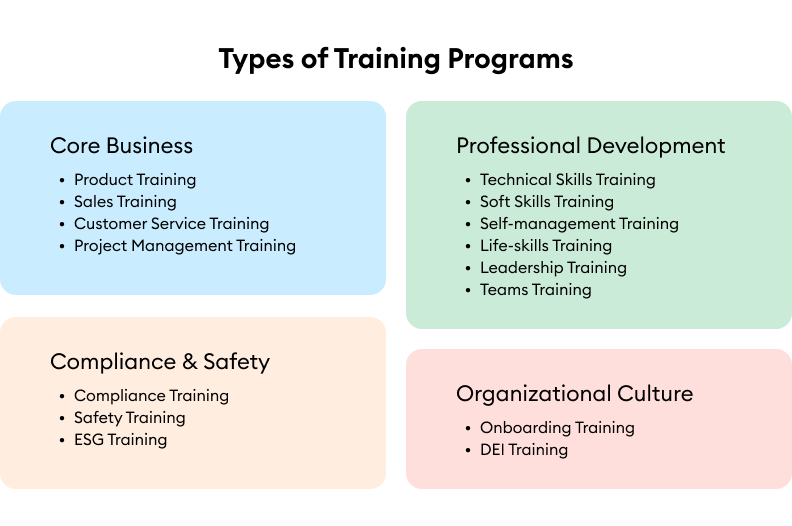
Training program types, grouped by purpose.
| Training Type | Training Purpose |
| Onboarding | Welcome and integrate new hires |
| Technical skills | Hone job-related skills |
| Soft skills | Improve workplace interactions |
| Leadership | Empower employees who are on track to becoming a manager or those recently promoted into a leadership position |
| Compliance | Meet regulatory requirements |
| Safety | Prevent workplace incidents |
| Customer service | Enhance client satisfaction |
| Sales | Boost revenue |
| Product | Ensure up-to-date and deep product understanding |
| Project management training | Improve delivery |
| Team training | Provide new team formation |
| DEI training | Foster an inclusive workplace |
| ESG training | Achieve decarbonization goals |
| Life-skills training | Personal development |
| Self-management training | Improve productivity |
What Are Employee Training Programs?
An employee training program is a planned set of learning activities that help employees get better at their jobs and grow professionally. Companies tailor these programs to meet both organizational objectives and employee needs.
Purpose of Training Programs
The purpose of training programs in companies extends across multiple strategic objectives:
- Get new hires up to speed quickly and confidently.
- Help employees master new tools and technologies.
- Build stronger teams and better workplace relationships.
- Keep everyone safe and have them follow important rules.
- Prepare team members for bigger roles.
- Build a positive workplace culture that keeps employees engaged, confident, and motivated.
- Stay ahead of industry changes.
- Make sure customers get great service.
If you’d like an in-depth guide, check this article on how to develop a training program for employees.
15 Types of Employee Training Programs
Now that we understand what a training program for employees is and its strategic objectives, let’s explore each training type in detail, including practical tips, use cases, and typical budget allocations based on company size and industry data.
Bonus: We calculated the budget numbers based on the Training Industry Report. They represent average figures. To get the values you’ll see in the different types of program descriptions, we took training expenditures per learner and projected budgets in learning areas.
Formula:
| Cost per Learning Area = Training Cost per Learner × Projected Budget Percentage |
Example: If Training Cost per Learner = $1,000 and Projected Budget for Leadership Training = 15% Then Cost for Leadership Training = $1,000 × 0.15 = $150 per learner.
Use these average numbers to calculate an approximate budget for your training initiatives.
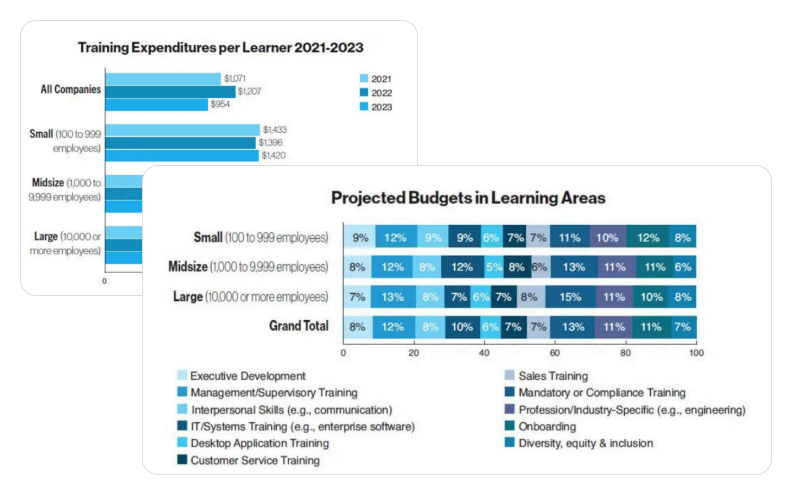
Data on training costs per learner and budget allocation by type.
1. Onboarding training
Onboarding training is the initial training phase that welcomes new hires and introduces them to the organization’s culture, values, policies, and role-specific duties. The purpose is to ensure that new employees feel equipped, engaged, and aligned with the company’s goals, creating a foundation for long-term success.
Onboarding training includes orientation training.
Example: A manufacturing company uses VR simulations to teach equipment operation to new workers.
Onboarding tips
- Give some thought to what kind of first impression you want new hires to have of the organization. The adage still holds true: “You never get a second chance to make a first impression.”
- Avoid information overload. Cover only what employees need to know to get started, then map out the rest of their learning experience.
- Consider having a company wiki so employees can refer to the information as needed.
- Focus on the new hire’s individuality. As they say, “Listen to their stories. Find out who they are. And then marry the two stories together.”
Use cases
- Ensure employee engagement and reduce turnover
- Return-to-work programs after an extended leave
Budget per learner
Percentage of total budget per learner per year.
Small companies: 12% = $170
Medium companies: 11% = $83
Large companies: 10% = $48
2. Technical training
Technical training focuses on teaching employees the specific skills and knowledge needed to perform tasks related to technology, tools, and processes that are essential to their role. This type of training is often job-specific, covering everything from software use and data analysis to machinery operation and digital skills.
Technical training tips
Stay informed with the latest technologies and regularly review your employee development program to keep it current.
Use cases
When new technologies and tools can significantly improve your employee’s productivity and reduce security risks.
Budget per learner
Percentage of total budget per learner per year.
Small companies: 9% = $128
Medium companies: 12% = $90
Large companies: 7% = $34
AI software training
While technical training spans many areas, artificial intelligence has emerged as a particularly critical focus area for organizations in 2024.
Studies show that 4 in 5 people want to learn more about how to use AI in their profession. According to a Salesforce survey, 62% of respondents say they don’t have the skills to use the technology effectively and safely. A great example of business gain is Github’s co-pilot product, which claims it can improve coding efficiency by 55%.
Since AI benefits both companies and employees, consider introducing AI tools for teams across your organization.
“Companies should build AI training into their L&D programs by teaching both the practical use of AI tools and the ethical considerations around them. This training needs to be customized for different roles across the organization.
At the same time, we need to strengthen core skills like critical thinking — employees need to know how to evaluate AI outputs effectively. We also can’t forget about soft skills, since the human ability to collaborate will become even more valuable.
And let’s be honest — employees are worried about AI taking their jobs. That’s why, beyond just technical training sessions, leaders need to show their teams how AI can actually help them transition into more meaningful, higher-level work,” shares Jeremy Walsh, EVP, Partner Solutions, AllCampus in this Training mag article.
3. Soft skills training
Soft skills training focuses on enhancing cognitive skills, behavior, and personal traits that allow employees to communicate and work effectively with others.
Soft skills are essential for promotion, work satisfaction, and a sense of meaning at work.
Example: A real estate company conducts negotiation workshops using actual previous deals.
Soft skills training tips
- Conduct regular soft skills training. “You need these tools to carry with you throughout your career, but the way you apply them may change,” says David Capranos, Director of Market Strategy and Research, Wiley Education Services.
- Always contextualize the training to trainees’ specific roles and show how it impacts them, their team, and their manager. This creates motivation for behavior change and makes the training immediately applicable.
- Ask managers to engage their team members on relevant tasks to apply their newly acquired soft skills.
- Use qualitative metrics, such as employee feedback and team performance reviews, to assess the impact of soft skills training.
Use cases
- Your company continuously experiences communication problems.
- The company plans to expand into new markets, and your coaching program may focus on cross-cultural communication and adaptive leadership.
- There are global challenges such as COVID, war, or economic crises that disrupt work and require specific skill development.
Budget per learner
Percentage of total budget per learner per year.
Small companies: 9% = $128
Medium companies: 8% = $60
Large companies: 8% = $38
4. Leadership skills training
Leadership training is designed to equip individuals with the leadership skills, strategies, and mindset necessary to lead teams, inspire others, and drive organizational success.
Bad leaders cost businesses billions of dollars every year and affect 70% of what makes employees engaged at work.
Managers must already possess the soft skills that they’re trying to develop in their direct reports. That’s why investing in leadership employee development training programs is so important for the company’s future.
Leadership training tips
- Outline the top-level business goals and identify the skills gaps that are keeping leaders from achieving those goals.
- Use self-assessment methods along with a survey of direct reports to identify training needs, and then create your leadership training roadmap.
- Assign real-world projects that allow leaders to apply what they’ve learned.
Use cases
- Employees who are on track to becoming managers
- Employees who have recently been promoted to a leadership position
Budget per learner
Percentage of total budget per learner per year.
Small companies: 9% = $128
Medium companies: 8% = $60
Large companies: 7% = $35
5. Compliance training
Compliance training is a mandatory program designed to educate employees on the laws, regulations, and policies relevant to their roles and the industry they work in.
Example: A pharmaceutical distributor creates interactive HIPAA compliance modules.
Compliance training tips
- Tailor training to include scenarios and guidelines relevant to specific roles, especially in areas like data handling or safety procedures.
- Update compliance training regularly to reflect regulatory changes and ensure ongoing relevance.
- Align compliance training with specific performance and business outcomes.
- Make compliance training more personalized and contextual.
- Put extra effort into making the often boring training engaging. Use gamification by making completion of the training a team activity. For example, the manufacturing company Zoltek uses the iSpring Spring authoring tool to create workplace classes that stimulate genuine interest and engage employees in compliance training.
Designing branching scenarios is easy in iSpring Suite, thanks to crystal-clear mind maps.
Use cases
- Highly regulated jobs and industries
- Government contract requirements
Budget per learner
Percentage of total budget per learner per year.
Small companies: 11% = $156
Medium companies: 13% = $98
Large companies: 15% = $72
6. Safety training
Safety training educates employees on workplace safety protocols, emergency procedures, and best practices to prevent accidents and injuries.
Example: A chemical manufacturer conducts monthly emergency response drills.
Safety training tips
- Use interactive methods, such as hands-on training, simulations, and gamified learning, to engage employees and reinforce key concepts.
- Create a culture where employees feel comfortable reporting new hazards.
- Regularly conduct safety drills (e.g., fire drills, evacuation drills) to ensure employees are prepared for emergencies.
- Tailor training modules to specific roles and risk levels, focusing on the most relevant hazards for each group.
Use cases
For organizations where physical safety is a concern (e.g., manufacturing, healthcare, construction).
7. Customer service training
Customer service training is designed to equip employees with the skills needed to deliver exceptional service, build customer loyalty, and handle customer inquiries or complaints professionally.
Target learners for this training type include employees who interact with customers or clients directly, as well as those who support customer service functions.
Example: An e-commerce business creates scenario-based online training using actual customer complaints.
Customer service training tips
- Use role-playing and real-life scenarios in customer service training to make sessions interactive and practical. By the way, you can easily convert these scenarios into dialogue simulations with iSpring Suite, a PowerPoint-based authoring tool.
An example of dialogue simulations in iSpring Suite
- Collect and use customer feedback to identify common service challenges and tailor training to address them.
Use cases
- An increase in customer complaints
- Company expansion into new markets
- Inconsistent service quality across team members
- New competitors entering the market with superior service
Budget per learner
Percentage of total budget per learner per year.
Small companies: 7% = $99
Medium companies: 8% = $60
Large companies: 7% = $34
8. Sales training
Sales training is a program aimed at improving the skills, techniques, and knowledge of sales professionals to increase their ability to foster client relationships, close deals, and meet targets.
Example: An insurance company conducts monthly sales pitch competitions.
Sales training tips
- Let sales reps learn by doing, watching experienced team members, and getting coached while working with real customers.
- Use role-playing and actual customer examples to make training relevant and engaging.
- Use assessments to identify specific needs and provide personalized coaching sessions that focus on areas for individual improvement.
Use cases
- Declining sales performance
- Changes in technology, legislation, and customer needs
Budget per learner
Percentage of total budget per learner per year.
Small companies: 7% = $99
Medium companies: 6% = $45
Large companies: 8% = $38
9. Product training
Product training focuses on educating employees about the company’s products or services, including their selling points, features, benefits, pricing details, and use cases.
Product training targets sales, customer support, and product and marketing teams.
Example: A tech company creates hands-on labs for new product features.
Product training tips
- Create a product knowledge base with screen-recorded instructions so employees can refer to them as needed.
- Use an LMS to quickly share updated training materials, and schedule brief refresher sessions as needed.
- Organize customer conversations and product demos to build confidence in discussing technical details.
Use cases
Every company needs product training — it’s essential for employees to understand what they’re selling and be able to explain it clearly to customers.
10. Project management training
Project management training provides employees with the skills to plan, execute, and close projects effectively. It covers the methodologies and tools needed for efficient project delivery, cost management, and team coordination.
Example: A marketing agency creates case-study-based project management workshops.
Project management training tips
- Assign mock projects or case studies to practice planning, budgeting, and risk assessment.
- Pair employees with experienced project managers to build practical knowledge over time.
Use cases
- Large-scale projects with multiple stakeholders, tight deadlines, and strict regulatory requirements
- Projects consistently miss deadlines or exceed budgets
- A significant number of projects fail to meet objectives
- Organizations aiming to improve efficiency and reduce costs
11. Team training
Team training focuses on improving group dynamics, collaboration skills, and collective performance. It helps teams work together more effectively by developing shared mental models, communication patterns, and coordination strategies.
Example: A software company conducts team-building workshops for cross-functional development teams.
Team training tips
- Use real team projects as training scenarios.
- Include both structured activities and informal team-building exercises.
- Focus on developing trust, communication, and conflict resolution skills.
- Practice decision-making as a group.
- Include remote collaboration skills for distributed teams.
Use cases
- New team formation
- After mergers or reorganizations
- When team performance metrics are declining
- For projects requiring high levels of coordination
12. Diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) training
DEI training aims to promote awareness, acceptance, and respect for diverse backgrounds and perspectives in the workplace. The goal is to foster a more inclusive and equitable environment, enhancing collaboration, respect, and innovation.
Example: A healthcare provider creates inclusive patient care workshops.
DEI training tips
- Don’t limit the training to gender-focused programs. Discover minorities within your company and collaborate with them to learn which modules and formats to choose for your DEI work training program.
- Put extra effort into making the often boring training engaging. Use gamification by making completion of the training a team activity.
Here is the detailed process of how to create an effective DEI program.
Use cases
- Mergers and acquisitions. When organizations merge, there may be a need to integrate diverse cultures and practices. This makes DEI training essential to foster a cohesive work environment.
- Employee feedback revealed employee concerns about inclusivity or experiences of bias.
Budget per learner
Percentage of total budget per learner per year.
Small companies: 8% = $114
Medium companies: 6% = $45
Large companies: 8% = $38
13. ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) Training
ESG training educates employees on the company’s commitment to environmental sustainability, social responsibility, and ethical governance. It aligns employees with the company’s ESG goals and encourages practices that support these objectives.
Example: A manufacturing company creates waste reduction challenge programs.
ESG training tips
- Highlight the benefits of ESG for the company, community, and environment, and how employees’ actions contribute.
- Share case studies showing ESG initiatives’ impact on communities and the environment.
- Create sustainability teams and task them with developing and implementing green initiatives across the company.
- Recognize and reward employees who lead sustainability efforts.
Use cases
- Regulatory requirements. Certain regulations require companies to report emissions and reduce carbon output based on their industry, size, and location.
- Investor demands. Investors are increasingly prioritizing companies with strong ESG practices. Organizations may initiate training to align employee efforts with investor expectations and enhance overall sustainability performance.
- Consumer awareness. As consumers become more conscious of sustainability issues, companies must train employees to meet these expectations and communicate their ESG initiatives effectively.
- Market share. Using ESG training is a way to differentiate your company in the market, enhance your reputation, and attract customers who value sustainability.
14. Life skills training
Life skills training provides employees with personal development skills that enhance their well-being and effectiveness, both at work and in their personal lives.
This training often includes financial literacy, communication, conflict resolution, and health management.
According to Udemy’s Workplace Learning Trends Report, personal growth skills remain in high demand as employees seek ways to cope with stress and burnout. Workers are focusing on self-awareness, emotional intelligence, and professional development to enhance their job performance and well-being.
Example: A tech company offers monthly financial planning workshops.
Life skills training tips
- Offer this type of training continuously so employees can use it on demand.
- Arrange the training to be anonymous if applicable because some employees may feel vulnerable to revealing their personal struggles.
- Identify top performers and their individual needs for this type of company training program.
Use cases
- Employee feedback and requests
- Decline in productivity in individual employees
15. Self-management training
Self-management training focuses on improving employees’ ability to set personal goals, manage their time, prioritize tasks, and stay productive. This training is essential for employee morale and for fostering autonomy and accountability.
According to SHRM’s Workplace Learning & Development Trends report, more than 4 out of 5 employees (81%) are interested in self-management training. Among organizations, more than 4 in 5 (83%) are likely to focus on workplace training that involves self-management skills within the next year, according to the HR managers surveyed.
Example: A consulting firm offers personalized prioritization coaching.
Self-management training tips
- Offer personalized assessments and create tailored development plans to address unique challenges.
- Encourage regular self-check-ins, reminders, and accountability partners to help employees stay on track.
- Incorporate practical tools like time-tracking apps, to-do list templates, and productivity planners.
- Include stress management and burnout prevention as core components.
- Use real workplace scenarios to practice self-management skills.
- Provide tools for managing digital distractions and maintaining work-life boundaries.
Use cases
- Increased remote/hybrid work adoption, which requires better self-organization
- Employee feedback indicating struggles with work-life balance
- A high volume of overtime hours, suggesting time management issues
Benefits of Employee Training Programs
After reviewing these 15 types of staff training programs, you might wonder what concrete value they bring to your organization. While each type serves specific purposes, all training and development programs for employees share some fundamental advantages of staff training that make it worth the investment.
Here are the most impactful benefits of training employees:
- Increased productivity and performance.
- Improved retention rates and reduced turnover.
- Better workplace safety and compliance.
- More attractive workplace for candidates.
- Stronger competitive advantage.
- Enhanced employee engagement and job satisfaction, which leads to increased employee loyalty.
15 Tips for Developing a Training Program
A successful employee training program means ensuring that your training process delivers information in a way that employees not only receive it but also grasp it and use it in their jobs.
Here are tips on how to make your staff training program work.
- Incorporate a mix of hands-on training activities, visual aids, and interactive training classes for employees.
- Regularly update training programs and methods based on feedback, technological advancements, and changing organizational needs.
- Give employees more control over their learning by allowing them to progress at their own pace. Offer in their benefits packages an annual personal learning stipend for employees to use as they like.
- Keep learners motivated. Consider approaches that inspire employees to pursue training, including connecting personal goals with organizational goals, making courses practical and relevant to their jobs and daily tasks, using technology to make lessons engaging and accessible, and even incentivizing learning by rewarding participants — with digital badges, for example.
- Customize staff training courses to match participants’ knowledge levels and roles.
- Offer constructive feedback to reinforce learning and address areas for improvement.
- Make training materials and resources easily accessible for all participants in order to remove extra obstacles. For example, make the program mobile-friendly.
- Choose suitable employee training methods (e.g., coaching, microlearning, on-the-job training) for selected types of training programs.
- Select a suitable training delivery method (synchronous, asynchronous, or blended learning) for the types of training programs chosen.
- Incorporate gamification elements, e.g., create friendly competitions.
- Promote knowledge-sharing among employees to enhance understanding and collaboration. For example, create interest groups in your corporate messenger, where employees can discuss challenges and share solutions and useful resources on specific professional topics.
- Encourage employees to seek additional resources and growth opportunities. For instance, agree with management on paid self-learning hours.
- Get your stakeholders aligned. Work in collaboration with other departments. Involve your SMEs, stakeholders, and especially your end users, so you’re more likely to hit their target.
- Run your training courses for employees regularly: every 1-3 months. This keeps employees’ skills sharp and establishes a learning culture.
- Use employee training software to streamline program delivery, track progress, and measure results across all training types.
FAQ on Types of Employee Training
What are the 3 types of training?
The three fundamental types of training programs for employees, classified by their purpose, are the following:
- Technical training focuses on job-specific skills and tools.
- Soft skills training develops interpersonal abilities and communication.
- Mandatory training covers compliance, safety training, and regulatory requirements.
What is the most common type of training?
Among all types of employee training, compliance training is the most common because it’s legally required across industries.
What are the 7 methods of training?
The 7 common methods of training are:
- On-the-job training
- Classroom/instructor-led training
- eLearning/online training (for employees to learn at their own pace)
- Coaching and mentoring
- Role-playing and simulations
- Job shadowing
- Blended learning (a combination of eLearning and ILT)
What makes employee training programs successful?
Successful employee training programs combine clear objectives, engaging content, practical application, and measurable outcomes. They align with business goals while meeting employee development needs through appropriate delivery methods and regular feedback.
Conclusion
This guide covered 15 different types of training programs that organizations need to consider. Each of these employee training program types serve specific organizational needs and contributes to overall business success through increased productivity, better retention rates, enhanced compliance, and a stronger competitive advantage.
What’s next?
- Assess your current training needs using our training needs analysis guide.
- Choose 2-3 priority job training types that align with your immediate business goals.
- Start small with a pilot program using the development tips provided.
- Consider implementing an LMS to manage your training programs effectively.
Need help getting started with team training? Contact our training experts for personalized guidance.





